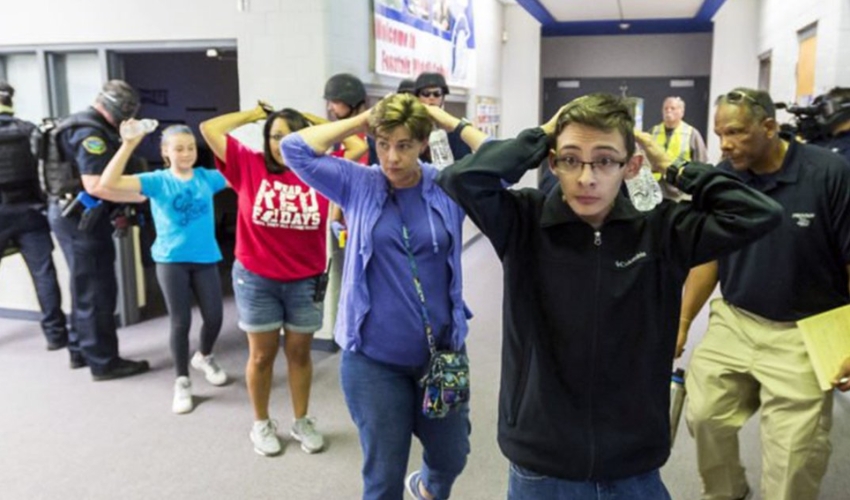
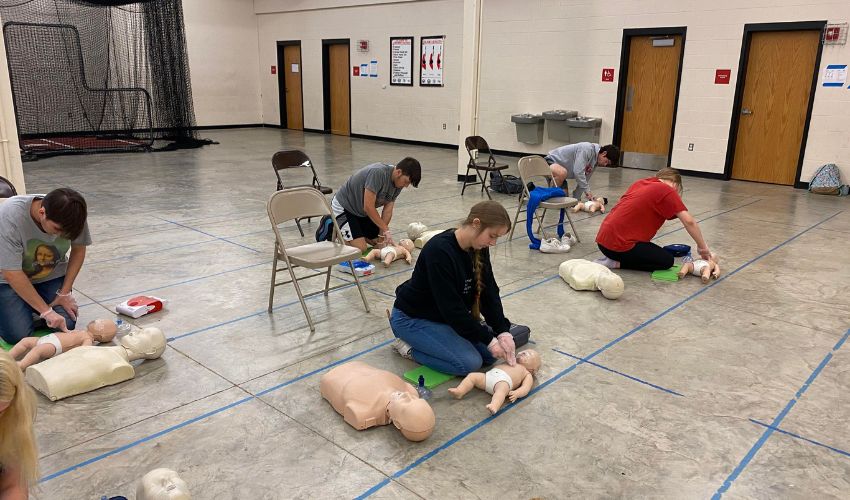
Active shooter events are on the rise in the US, affecting schools, workplaces, and public spaces. Organized, institutional, and community active shooter preparation today requires regular drills. Emergency reaction drills prepare people for high-stress, life-threatening situations. Real-world drills, such as school shooting drills or workplace safety training, enhance reaction time, mitigate fear, and refine crisis management strategies, ultimately saving lives. Include shooter simulations, evacuation drills, and emergency lockdown scenarios in everyday operations to improve situational awareness. Citizen training also enhances outcomes by encouraging critical thinking and decision-making under pressure. Adequate crisis communication and evacuation preparations also benefit organizations. Drills reinforce the ‘Escape, Barricade, Defend’ procedure, a set of actions recommended by security experts nationwide. Precision in safety drills requires practice and an honest assessment of the dangers involved. Crisis survival requires preparation, not fear. Teachers and supervisors should learn to remain calm, act decisively, and save lives. Workplace and campus safety culture must require regular training. Speeds Emergency Response and Reduces Panic: Regular active shooting workouts greatly enhance high-stress response time speed for individuals and teams. Chaos and casualties typically follow delayed replies. Emergency reaction drills train the brain to act rapidly. Knowing what to do reduces panic behaviour. The Escape, Barricade, Defend protocol improves decision-making confidence and automaticity. Even under gunfire or yelling, staff and children learn to act quickly. Milliseconds matter in real life. A trained mind and body respond faster than shock. Participants also learn to notice warning indicators and respond to fast changes in drills. Rehearsal turns uncertainty into focused execution. Drill participants are proactive. They move after freezing. Shooter simulation exercises enhance muscle memory and spatial awareness by requiring real-time decision-making. With trained people, emergency responders can coordinate quickly. First aid, communication, and mobility improve. These workouts provide people with a sense of control in unmanageable situations. Crisis confuses; training clarifies. Practice reaction activities before a catastrophe occurs to respond quickly, focused, and courageously when lives are at stake. Communication and Choosing Strengthen Crisis: Crisis communication is crucial during active shooter scenarios, and regular drills are helpful. When uncertainty spreads, clear communication saves lives. Regular safety exercises help participants develop clear, meaningful communication under pressure. Every phrase counts when reporting to the police or alerting others. Leaders, such as school principals or workplace supervisors, play a crucial role in active shooter scenarios. They may test and improve communications by practicing evacuation drills. Intercoms, alarms, and emergency messages must operate. If not, silence or misinterpretation might kill. Practice drills help teams identify and improve issues. Regular drills teach people to quickly report the shooter’s position, the number of shots, injuries, and safe routes. Leaders must ensure that these drills are conducted effectively and that all participants understand their roles and responsibilities. Only repetition makes Escape, Barricade, Defend second nature. Participants learn to analyze and act on real-time information. Decision paralysis is typical in high-stakes situations. Crisis management promotes clarity, structure, and cooperation to avoid that. Drills reveal plan flaws and leadership shortcomings. Decision-making practice reduces second-guess reluctance. Clear orders, calm voices, and trained decisions separate chaos from control. Confusion prevails without communication. Consistent training helps people think, communicate, and behave as a team. Helps Create Effective Evacuation Plans: Regular exercises strengthen an active shooter evacuation strategy. Even the finest plans may collapse amid chaos without practice. Evacuation drill procedures need to become normal, not just written down. People must know where, how, and when to move. Regular shooter simulations demonstrate how quickly attacks may transform reality. These drills reveal flaws in exits, hallways, and safe rooms. Planners learn about choke spots and hidden risks. A well-trained evacuation strategy enhances survivability and fosters leadership trust. It promotes accountability and collaboration, fostering a sense of unity and shared responsibility. Everyone contributes, leading, following, or helping. Evacuation rehearsals help eliminate confusion and expedite action. Rapid, quiet evacuation can save lives in emergencies without the need for lockdowns. These experiences train personnel to remain calm, act quickly, and assist others in escaping. Leaders test instructions for clarity and audibility via drills. Practice escapes with locked doors, packed corridors, and loud noise to prepare for real problems. Only constant practice makes an evacuation plan successful. New insights, improvements, and confidence come with each practice. Crisis instincts aren’t enough. Practice makes survival feasible, but planning saves lives. Because safety depends on preparedness, practice every route, stride, and voice. Prepares staff and civilians for real-world threats: Civilian training is crucial for surviving an active shooter situation. Regular drills prepare brains and bodies for danger. Every civilian should know how to handle danger. Fear-reduction drills boost bravery. You must experience these protocols, not learn them from a placard. Shooter simulation exercises enhance realism, which is important for psychological preparation. Participants hear gunfire, experience quick events, and sense dread. This conditioning prevents emergency panic. Regular safety exercises empower citizens to make quick, educated decisions and help them become familiar with the sounds and sensations of a real shooting situation, reducing the likelihood of panic and increasing the chances of survival. Civilians gain confidence and avoid uncertainty by training repeatedly. Threat assessment becomes automatic. More civilian training aids law enforcement’s tactical reaction. Drills enable janitors, instructors, receptionists, and supervisors to help, instilling a sense of confidence and preparedness in the face of potential threats. Every trained civilian reduces victimization and increases protection. Trained civilians act in emergencies. Readying converts fear into power. Train like your life depends on it because it does. Not only do professionals practice emergency response drills, but they also do so regularly. Civilians need them too. Strengthens lockdown and shelter-in-place procedures: Active shooter response requires emergency lockdown skills. Regular drills apply theory. Emergency response drills educate personnel on swift and efficient lockdown procedures. Delayed acts can be disastrous. In a lockdown, stillness and time are crucial. Everyone understands their function and location after this training. Practice lockdowns to lessen noise, confusion, and fear during the event. Train repeatedly to build muscle memory. This helps individuals move without thinking under pressure. Regular
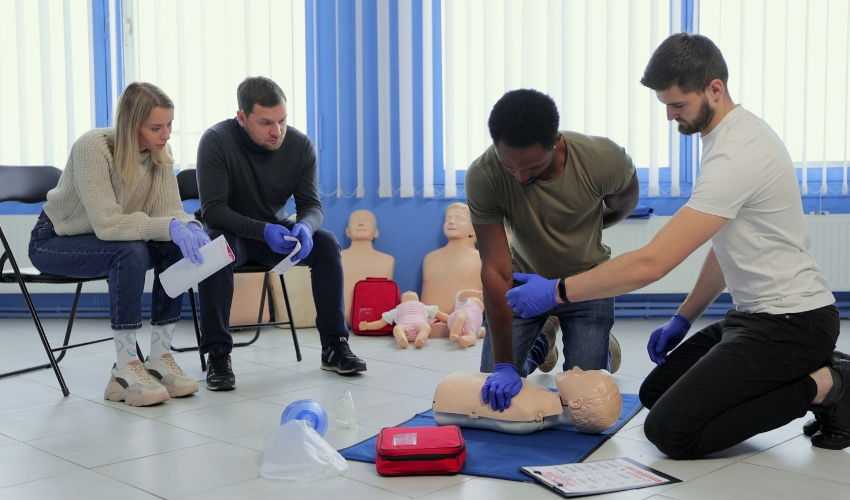
Common Misconceptions About CPR & BLS
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) and Basic Life Support (BLS) are two topics that many individuals are confident in. Even among skilled persons, there are still many lifesaving CPR myths, BLS certification misunderstandings, and CPR training misconceptions. These beliefs can slow response, diminish efficacy, or risk lives. Due to fear and hesitation about CPR, many spectators avoid helping. Others feel rescue breaths are optional, or chest compressions must be moderate. Untrained users should not utilize an Automated External Defibrillator (AED). AEDs are safe for anybody to use in emergencies. Hands-only CPR myths deter onlookers from helping without rescue breaths. In Sudden Cardiac Arrest (SCA) incidents, 911 Emergency Services and first responders request rapid assistance from close witnesses. CPR myths and facts can save lives. Knowing what works and doesn’t is vital. Power yourself with facts, not myths. Let’s discuss the most common misunderstandings so you may become a life-saving hero. Unsafe Bystander CPR Myth: “Only Professionals Should Perform CPR”: A dangerous bystander CPR myth is that only trained professionals should do CPR. Every second matters. A victim’s survivability may decrease while waiting for first responders to arrive. The American Heart Association (AHA) recommends that laypeople start CPR very easily. Hands-only CPR can keep blood flowing until aid comes without certification. Many misconceptions about CPR training inhibit action, often due to concerns about doing it incorrectly or causing harm. However, poor CPR is better than none. Even poor chest compressions enhance survival. The Good Samaritan Laws safeguard innocent bystanders. A BLS Provider Course or CPR training empowers you to help legally and morally. The AHA found that immediate CPR can double or triple the chances of survival. Although rescue breaths are crucial, hands-only CPR is frequently successful for adults. 911 Emergency Services dispatchers can aid you while help arrives. Lifesaving CPR myths that discourage action are dangerous. Knowing the myths and facts about CPR enables you to take fearless action. Don’t underestimate your lifesaving abilities. Actively participate. “You Must Include Rescue Breaths Every Time” A Common CPR Training Misconception: Overemphasizing rescue breaths in every circumstance is one of the most common misconceptions in CPR training. Rescue breaths are essential to standard CPR, but not always. The American Heart Association (AHA) recommends hands-only CPR for adult cardiac arrests in public. Lifesaving CPR myths include the notion that skipping rescue breaths makes CPR ineffective. Not true. However, most adult cardiac crises require urgent chest compressions. Confusion regarding CPR procedures can cause fear and hesitation during CPR. Death can result from this delay. Understanding situation differences promotes confidence and reduces uncertainty. Incorrect CPR techniques, such as pausing for needless rescue breaths, reduce efficacy. Additionally, misunderstandings about BLS certification cause hesitation. BLS Provider Courses explain the use of rescue breaths. Operators from 911 Emergency Services can give real-time assistance. Follow their directions and start chest compressions. Do not allow misconceptions to influence your judgment. AED usage misconceptions include breaths before defibrillation. Clear information can save lives in the early minutes. “Using an AED is Complex and Risky” Debunked: Many people are reluctant to respond to cardiac crises because of misunderstandings about Automated External Defibrillator (AED) use. Some think AEDs are too complex or harmful. Untrue. The public can use AEDs without training. Clear voice instructions take you through each step. Some CPR myths and facts include that using an AED is easy and safe. The American Heart Association (AHA) includes AED training in its BLS Provider Course because it saves lives. With an AED nearby, fear and hesitation rise. Incorrectly startling someone worries people. However, AEDs assess cardiac rhythms and shock only when needed. You cannot damage someone by following computer prompts. Delaying AED use is a typical BLS blunder that reduces survival. Defibrillation restores cardiac rhythm, but hands-only CPR maintains circulation. Using an AED within the first few minutes significantly boosts survival rates. CPR training misconceptions often obscure public access to AEDs. Compress your chest and use an AED immediately. Knowing the truth regarding AED use empowers you to act boldly and effectively. Myths aside, AEDs save lives daily. CPR Fear and Hesitation: “You Can Hurt Someone with CPR”: CPR fear and hesitation stem from the fear of harming the patient. For fear of fracturing ribs or exacerbating the disease, many spectators avoid chest compressions. Broken ribs are a small price to pay to save a life. These concerns reinforce CPR myths and facts, such as that doing CPR improperly is worse than doing nothing. Simply not true. The American Heart Association (AHA) recommends CPR. Until emergency responders arrive, chest compressions keep oxygen-rich blood circulating to important organs. Emergency BLS certification misunderstandings can also confuse. BLS Provider Courses promote effective CPR procedures, reducing errors. Compressions that are too soft or too slow are common BLS errors. However, responding promptly gives the sufferer a greater chance of recovery. If uncertain, 911 Emergency Services will help. These laws are in almost every state and should calm your anxieties. CPR training misconceptions increase intervention risks. Your actions might double or triple someone’s chances of survival. Chest compressions should start quickly, although rescue breaths and AEDs can aid. Getting beyond your hesitancy might save your life. Avoid fear and act promptly and boldly to save lives. “BLS Training Is Only for Healthcare Workers”: A Common BLS Certification Misconception: This BLS certification misconception is severe. Teachers, coaches, and caregivers benefit from Basic Life Support (BLS) skills. Lifesaving CPR myths say only doctors should help in emergencies. Not true. Bystanders who have completed training do many successful resuscitations. CPR training misconceptions prevent individuals from participating in accredited programs. Some find the content too advanced or unimportant. Home cardiac crises are more common than hospital ones. Untrained or undertrained people make common BLS errors. Incorrect CPR techniques prolong recovery and lower the likelihood of survival. Rescue breaths, chest compressions, and AED use need precision. 911 Emergency Services may take time. Bystanders must lead till then. These safeguards make action safer and wiser. CPR myths and facts make you a lifeline, not just
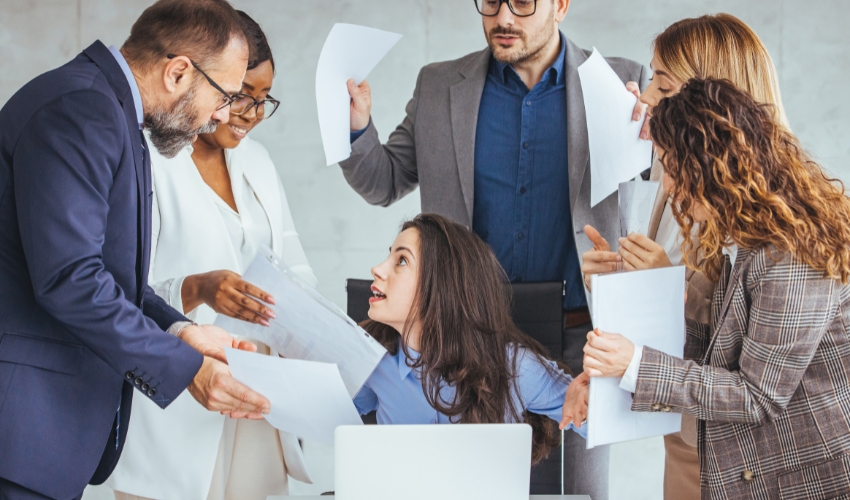
Importance of Conflict Management to Boost Workplace Success
Every workplace has conflict, but handling it is essential for long-term success. How leaders and workers handle team conflicts affects whether they benefit or hurt. Unresolved conflicts can damage morale, productivity, and departmental relationships. Using conflict resolution approaches can improve workplace health and cooperation. Stressing workplace conflict resolution reminds employees that their problems matter and that communication is a two-way process. Conflict resolution skills help employees handle differences without fear. Strong conflict management includes mediation, active listening, and emotional intelligence to help employees understand one another. These strategies create positive outcomes of conflict instead of tension. Effective conflict handling techniques enhance teamwork and decision-making. Businesses should avoid power imbalances that impact fair solutions by encouraging open communication and assertiveness. Conflict management enhances job satisfaction, fosters cooperation, and reduces turnover. Effective team conflict management fosters trust and prevents setbacks. Focusing on organizational conflict avoidance prevents catastrophes. Instead of competing, win-win strategies help everyone find solutions that benefit all parties. Promoting employee mediation strategies helps achieve fair results in challenging situations. Why Conflict Management Is Important? Workplace Conflict Resolution Promotes Trust and Professionalism: Effective workplace dispute resolution builds leadership and employee trust. Conflict resolution techniques prevent anger from arising from arguments. This promotes open conversation and respect. Leaders may de-escalate tension before it affects team performance via mediation and active listening. Conflict resolution fairness boosts workplace trust. An effective conflict resolution culture helps reduce emotional outbursts and reputational damage. Emotional intelligence enables managers to empathize and respond effectively. This soft ability improves conflict resolution, especially in challenging talks. Assertiveness helps preserve professionalism without being overly passive or hostile. Conflict resolution abilities help personnel avoid rumors and tackle issues directly. Honest communication fosters workplace respect. Leaders guarantee everyone’s voice matters by addressing the power imbalance. Employees feel empowered, not controlled. Fair problem-solving promotes honesty and respect. Teams prosper when conflicts don’t hurt their reputation or connections. Professional conflict resolution promotes employee engagement and decreases attrition. Teams learn constructive conflict resolution via regular training. When workplace dispute resolution is a standard practice, trust, fairness, and professionalism naturally follow. Conflict Management Enhances Team and Organizational Success: The benefits of conflict management extend beyond rapid resolution. Leaders who prioritize conflict resolution foster a healthier and more productive workplace. Improved team dynamics eliminate misconceptions and improve project and decision-making cooperation. Effective conflict management enhances staff retention and morale. People feel safer in companies that value their voices and perspectives. Emotional intelligence and active listening make everyone feel understood in stressful situations. Mediation demonstrates that leaders are fair, thereby reducing employee conflict. Managers can mitigate tension before it impacts production by employing effective interpersonal communication strategies. Conflict resolution skills enhance organizational values like respect and responsibility. Organizations prevent interruptions and legal expenses by using conflict management tactics. Assertive employees can speak honestly without being confrontational. All levels feel empowered by transparency. In a win-win conflict resolution, corporations include both parties. Collaboration leads to better judgments and longer-term benefits. Overall, advantages spread across departments and functions. Trust and fairness improve communication, innovation, and teamwork. Stressing conflict management improves performance, employee happiness, and long-term success. Every company benefits from early, fair, and productive conflict resolution. Peacemaking Skills Empower Staff and Avoid Escalation: Employees with dispute resolution skills can help prevent stress from escalating. Staff can remain calm and think clearly under pressure by utilizing these abilities. Education training emphasizes the importance of disagreement, impartiality, and fairness. When workers can resolve their disputes, they rely less on management. Active listening reduces defensiveness and emotional outbursts by making everyone feel heard and understood. Teams that practice emotional intelligence are empathetic. These abilities enable deeper communication and fewer misunderstandings. Being assertive helps people express their demands while respecting others. Without these tools, individuals avoid conflict or react negatively. Communication experts are courteous and problem-solving. Interpersonal communication helps teams work together. Strong conflict skills reduce divides in organizations. Conflict resolution may also train people for leadership and advancement. Leaders who demonstrate these abilities encourage others. Skills-based training reduces the need for HR and legal mediation. Teams learn to solve issues independently. It also prevents morale and workflow problems. Preventing conflict escalation saves time and boosts job satisfaction. When employees effectively manage team conflict, the firm benefits. Organizations should constantly train employees in modern conflict management. Communication in conflict affects outcomes and relationships: The importance of communication in conflict is very high. Communication is crucial to conflict resolution; it starts and ends. Poor communication leads to team assumptions, animosity, and dissatisfaction. Learning interpersonal communication promotes understanding and collaboration during conflicts. Employees support others’ viewpoints and alleviate emotional strain by actively listening to them. Listening helps people reply sensibly, not defensively. Effective communication takes assertiveness to respectfully and confidently address issues. Clear communication reduces misunderstandings and streamlines processes. Communication eliminates misunderstanding and improves teamwork. Communication skills help identify potential disputes early on. Using emotional intelligence, they read tone, body language, and unstated requirements. This minimizes escalation and promotes empathy in stressful situations. Mediation managers utilize open discussion to explain expectations and reconcile divisions. Negotiations also involve communication to identify common ground. Structured interactions keep solutions reasonable and focused. Win-win strategies respect all voices. Open communication fosters a transparent workplace where conflicts are manageable. Disagreements become learning opportunities for employees. Encourage regular feedback and communication to help the team self-correct and improve. With good communication, companies regard conflict as constructive. Conflict becomes collaboration, confusion gives way to clarity, and separation yields togetherness through clear communication. Employee mediation resolves disputes fairly and respectfully: Strong employee mediation tactics handle disagreements swiftly and fairly. Mediation provides a neutral forum for parties to discuss and resolve issues. Active listening and emotional intelligence help skilled mediators comprehend both sides. This fosters empathy and collaboration amongst opposing personnel. Mediation protects professional relationships and fosters a positive workplace environment. It helps with power disputes and repeated tensions. Interpersonal communication enables people to discuss topics without resorting to personal attacks. Fair mediation promotes organizational values, including respect, responsibility, and inclusivity. Professional mediators prevent power
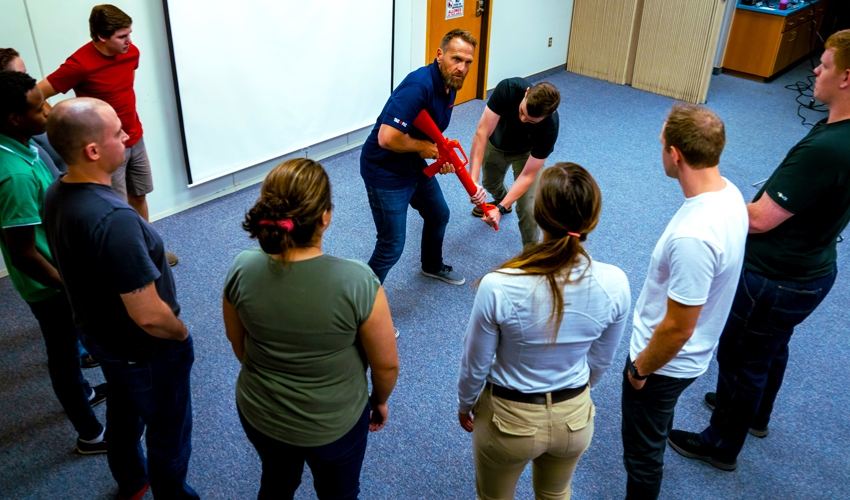
7 Reasons Why Active Shooter Training is Important
Shootings are unpredictable, rapid, and typically over in minutes. Individuals and organizations must plan well now. Business, school, and public venue managers may save lives by becoming active shooter-ready. FEMA, DHS, and FBI-backed training programs provide survival tools. Training that promotes situational awareness, quick decision-making, and successful emergency response is the foundation of this preparation. ALICE Training Institute, NTAC, and the U.S. Department of Education advocate proactive preparedness. Staff and kids can respond promptly using the Escape, Barricade Defend, and Stop the Bleed programs. Implementing school security exercises, crisis management strategies, and workplace safety practices reduces injury and speeds up response. A safe citizen response enhances law enforcement effectiveness. Threat assessment training also recognizes pre-violence indications. Community services like Safe2Tell allow people to report dangers early. Survival skills are an integral part of active shooter simulations and citizen defense training. Active shooting training boosts confidence, sharpens intuition, and makes everyone safer. 7 Reasons Why Active Shooter Training is Important Improve Situational Awareness Before a Crisis: Active shooter preparedness begins with situational awareness in regular life and high-risk situations. People typically neglect their environment, which can lead to delayed responses. Participants learn to monitor their behavior, identify escape routes, and remain alert through emergency reaction training. DHS and NTAC promote awareness as a core ability. During active shooter simulations, people perceive subtle risks to escape harm and defend others. ALICE trains people to evaluate rooms, comprehend exits, and make quick safety judgments. Escape Barricade Defend protocol requires active decision-making, which situational awareness aids. Knowing whether to conceal or flee depends on awareness. Regular school security exercises teach kids and staff safety behaviors. Workplace safety policies encourage hazard assessments and awareness briefings. Civilians can defend themselves by reporting suspicious activities through the Safe2Tell program. Provide correct facts early to optimize law enforcement response times. Awareness training helps employees think and respond quickly, preventing panic. Every second counts in shooting. Situational awareness allows people to avoid danger. Realistic Training Scenarios Improve Emergency Response: Effective emergency response training turns spectators into guardians. Realistic drills develop pressure-thinking and movement. These workouts enhance muscle memory, quickness, and confidence by simulating real-life challenges. Immersive training by FEMA, the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI), and the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) promotes active shooter readiness. They promote community-based reaction and law enforcement collaboration. School security exercises comply with the U.S. Department of Education’s requirements. Active shooter simulation training educates individuals on fear processing and decisive action, thereby improving reaction times. Law enforcement and trauma experts collaborate with the ALICE Training Institute to create these simulations. Regular emergency response training improves workplace safety. Employees learn their duties, communication skills, and evacuation and barricade techniques. Running in zigzags or utilizing objects as shields becomes a common Civilian defense tactic. Participants can offer help following an occurrence with Stop the Bleed. Training involves the use of tourniquets and pressure to stop blood loss. This decreases pre-EMS deaths. Training through simulation improves threat response at all levels. Reality-trained people handle stress, save lives, and reduce mayhem. In genuine emergencies, survival preparedness matters more than practice. Proactive Training Improves Threat Identification: Identifying threats before violence saves lives. Threat assessment training teaches the recognition of early warning signals. The National Threat Assessment Center (NTAC) and the FBI emphasize the importance of preventive responses. Active shooter readiness training teaches employees and students to recognize and report unusual behavior. Sudden retreat, harsh words, and weapon fixation are behavioral signs. The Safe2Tell program allows anonymous reporting. U.S. Department of Education encourages multi-disciplinary threat management and evaluation teams. These teams include counselors, police, and administrators. Rapidly reviewing findings and implementing interventions. ALICE and the DHS stress attentiveness. Staff keep prepared with regular updates to workplace safety protocols. Threat assessment training keeps worries alive. School security exercises emphasize the importance of reporting suspicious activity. These drills promote safety and eliminate the stigma of reporting. They also adhere to crisis management and emergency response protocols. Threat reporting must be accurate and quick for law enforcement. Civilian defense begins with identification and escalates from there. Prevention is the most effective method for addressing active shooters, and training is the first step. Promote Crisis Management to Reduce Panic: Panic during an active shooter situation can cause injuries and disorientation. Managing crises helps preserve order. Communication plans, leadership positions, and procedures are examples of these. ALICE trains leaders under pressure. Clear directions aid survival. DHS and FEMA offer school and workplace crisis plan templates. Escape or Barricade under pressure, Defend etiquette aids speedy decision-making. Knowing how to flee, hide, and fight decreases reluctance. These steps reduce group paralysis and casualties. Repeating workplace and school safety practices calms. Experience with emergency procedures builds confidence. Even when scared, trained people can recall procedures. Psychological preparation is a crucial component of training for active shooters. Learning to breathe, move, and think boosts survival. Crisis management promotes leadership in disorder. Civilians’ clear and precise information aids law enforcement’s response. The Safe2Tell and Stop the Bleed campaigns aid crisis management. A skilled civilian stabilizes the scene while police respond. National School Safety Center recommends clear command chains and dependable transmission. These methods expedite safety, as training minimizes emotional stress and ultimately saves lives. Include Training in School Safety Systems: Schools must lead active shooter preparedness efforts to safeguard children and staff. School safety training boosts community resiliency. Drills, rules, and teamwork lower risk and increase results. School security drills educate students to behave swiftly and obey adults. They practice lockdowns, evacuations, and communication. These exercises must follow guidelines established by the U.S. Department of Education and local law enforcement. The ALICE Training Institute offers age-specific school programs. These modules teach survival skills while respecting emotions. Students and instructors can anonymously report questionable activity through Safe2Tell. These ideas are part of threat assessment training in schools. FEMA (Federal Emergency Management Agency), DHS, and NTAC assist school administrators in planning. Policy formulation, simulation planning, and EMS/law enforcement partnership are their resources. Staff and even older students may help in
6 Reasons Your Staff Should Be CPR Certified
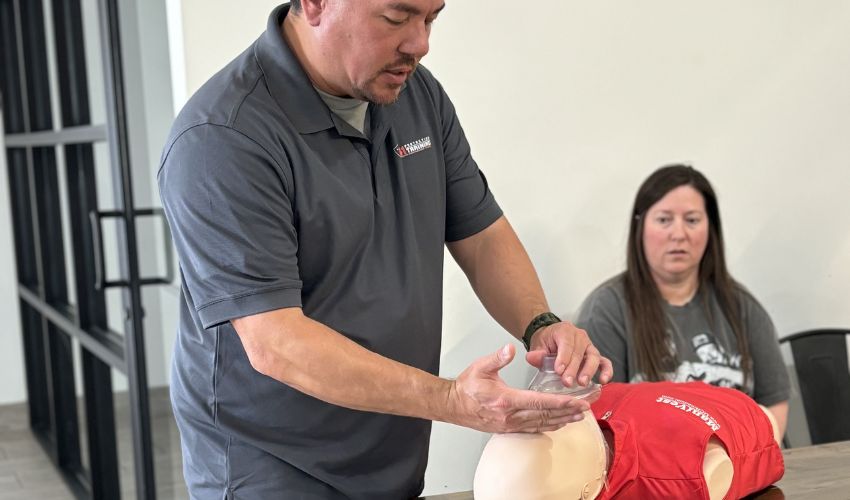
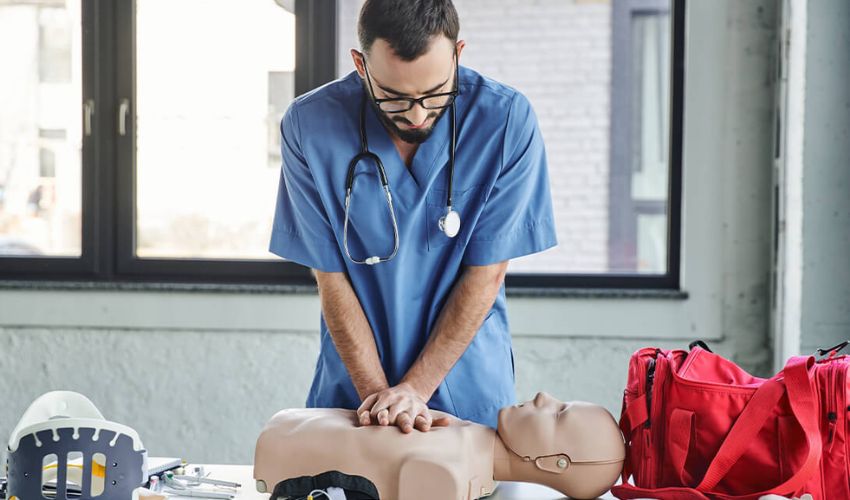
The importance of CPR at work is essential because emergencies can occur at any moment, even during a workday. Every workplace is vulnerable, and life-saving skills for staff must be available. Preparation and emergency response training save lives in small and large businesses. A coworker may collapse, choke, or have cardiac arrest without warning. In key circumstances, trained staff make all the difference. Employee CPR certification is a key tool in safety. There are many benefits to CPR training, including the ability to stabilize the situation and buy time until aid arrives. Your emergency medical services (EMS) may arrive after several minutes. Trained staff can respond to prevent death or lasting injury in that gap. CPR training for employees promotes morale. If something goes wrong, teammates can aid, making employees feel safer. This fosters trust and caring. You appreciate people, not just productivity. 6 Reasons Your Staff Should Be CPR Certified 141 Protection Training trains teams to act bravely. Our First Aid and CPR training is practical and meets OSHA CPR requirements. We train your team to respond quickly, stay cool, and save lives. Here are some compelling reasons why every firm should train its employees in CPR certification. Save Lives During Sudden Cardiac Arrest (SCA) SCA is a life-threatening illness that can strike without notice. The U.S. has around 350,000 out-of-hospital cardiac arrests annually. The American Heart Association (AHA) says timely CPR can double or triple a victim’s chances of survival. Every minute without CPR affects survival by 7–10%. This makes staff CPR certification a life-saving need, not merely a safety measure. SCA causes the heart to stop abruptly, cutting off the blood supply to the brain and other organs. Death may happen in minutes without help. Certified CPR Training Center employees respond quickly. They can save lives until EMS arrives by recognizing cardiac arrest, starting chest compressions, and using an AED. Evidence-based CPR and BLS training is available from the Red Cross, CPR Certification Institute, and National Safety Council (NSC). These programs train staff to perform CPR safely, use an AED, and stabilize a victim. CPR certification increases the odds of survival and promotes workplace safety. If a coworker, customer, or visitor collapses, your personnel will act decisively, confidently, and compassionately. Disaster or survival may depend on that preparation. Create a Safer and More Prepared Work Environment A safe workplace requires more than fire extinguishers, first aid kits, and evacuation maps; it requires a trained staff to act quickly. This vital preparedness comes from CPR certification. You may teach your team to save lives in crises by certifying them through AHA, Red Cross, or NSC-accredited CPR Training Centers. Employees become first responders when they know CPR, AED operation, and Basic Life Support (BLS). This makes your workplace safer and more responsive. EMS may not always arrive in emergencies, but a qualified employee might be able to save the day. Certified employees demonstrate accountability, quick thinking, and composure under pressure, thereby boosting team spirit. Knowing your coworkers can aid in emergencies is powerful. In some businesses, OSHA safety requirements mandate or encourage personnel to receive CPR and first aid training. This lowers liability and demonstrates to authorities and stakeholders that your company values safety. Indeed, CPR-certified workers create a safe, confident, and resilient workplace that prioritizes human life and operational efficiency. Improve Emergency Response Time and Reduce Workplace Liability In medical emergencies, including cardiac arrest, seizures, and choking, reaction speed is crucial. The AHA states that brain damage can begin four to six minutes after the heart stops. That typically happens before EMS arrives. Survival increases with the speed at which a qualified person starts CPR and utilizes an AED. Reducing this time gap is where CPR-certified personnel shine. CPR and BLS training boosts emergency readiness for employers. Nationally renowned CPR Training Centers, including the Red Cross, CPR Certification Institute, and National Safety Council (NSC), teach personnel how to spot situations, respond quickly, and stabilize until EMS comes. These skills can greatly lessen incident severity. Early action saves lives and avoids legal danger. Employers must offer a safe and healthy workplace, and CPR training helps meet these demands. Company attentiveness and care can protect businesses against negligence or insufficient response claims when employees are educated and prepared. A quick and competent emergency reaction increases your company’s image. Clients, consumers, and workers value a safe workplace. Limiting liability is just the start—gaining peace of mind and trust is priceless. Empower Staff with Confidence and Leadership Skills CPR certification improves confidence and leadership, not just abilities. Employees who undergo AHA, Red Cross, or CPR Certification Institute training generally feel more equipped to manage stressful and unpredictable circumstances. People who can respond under pressure save lives and set an example. Emergency confidence ripples across the workplace. Trained personnel make better decisions, communicate better, and stay calm while others panic. These are hallmarks of good leaders. You’re teaching your crew these skills by investing in CPR and BLS training. Participants experience chaotic leadership via scenario-based training and AED demonstrations at authorized CPR Training Centers. Beyond theory, realistic simulations teach individuals to remain calm, assign responsibilities, and perform critical operations under pressure. This leadership goes beyond emergencies. In customer service, team management, and conflict resolution, high-stakes managers perform better. Employees who take initiative, build trust, and prioritize safety benefit employers. Including CPR certification in professional development is a smart move. It demonstrates your company’s commitment to OSHA and NSC compliance, encouraging employees to lead with resilience, empathy, and purpose. Meet OSHA and Industry-Specific Safety Requirements CPR certification is a key to compliance in many businesses with severe safety rules. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) encourages CPR and first aid training in many workplaces, especially those without immediate access to medical response. Training personnel at reputable CPR training centers ensures legal compliance, decreased liability, and emergency readiness for organizations. Healthcare, construction, childcare, dentistry, hospitality, and manufacturing typically demand CPR and BLS certificates—state and federal legislation support OSHA’s rules. Your firm fulfils and
Why is CPR Considered a Life-Saving Technique?
CPR and preventing brain damage, it stands as a vital time-sensitive intervention during cardiac arrest, where every second determines survival. The importance of CPR in cardiac arrest lies in how CPR maintains blood flow to the brain until professional emergency response arrives. Studies prove that, how CPR saves lives, with CPR survival rate statistics showing a 2- 3x higher chance when bystander CPR begins immediately. The CPR benefits in emergencies include delaying brain damage by manually pumping oxygenated blood to vital organs. Why early CPR is critical becomes clear when comparing CPR vs. no CPR outcomes; victims without compressions face near-zero survival after 10 minutes. CPR plays a key role in the chain of survival, bridging the gap between collapse and defibrillation. Real-world CPR success stories highlight how quick action prevents irreversible harm. By forcing blood flow to the brain, CPR stalls cell death during a heart attack or respiratory failure. Proper technique sustains minimal oxygen circulation, buying time for advanced care. Understanding these facts at home or in public turns hesitation into life-saving action. CPR Maintains Blood Circulation During Cardiac Arrest: When the heart quits, CPR keeps blood flowing. Chest compressions reflect the normal beat of the heart. This hand-pumping stops organ failure. Oxygen keeps reaching important tissues. Right away, CPR reduces the risk of brain damage.Every compression forces blood through arteries. Correct technique guarantees enough flow. Depth counts; press minimum two inches. Speed counts—keep 100 to 120 compressions per minute.Blood travels to the brain carrying oxygen. Brain cells die swiftly without CPR. The heart needs this help to get going again.Double survival chances with bystander CPR. Don’t hesitate; go swiftly and forcefully. Even flawed CPR benefits. Keep on till aid shows up. Your acts help to sustain life amid distress.In a cardiac attack, every second counts. Good compressions replicate artificial circulation. This basic behavior closes the distance to advanced. CPR Prevents Brain Damage by Oxygenating Blood: While breathing stops, CPR maintains oxygen delivery to the brain. Chest compressions pump blood carrying essential oxygen to organs. In minutes without oxygen, brain cells die. Rescue breaths bring new oxygen into the circulation. Even hands-only CPR efficiently moves oxygen that is already available.A good method preserves oxygen flow during cardiac arrest. Every compression drives blood high in oxygen toward the brain. This slows down brain damage until normal circulation starts. Starting CPR right away helps the brain to live for longer.Oxygen deprivation rapidly results in irreversible brain damage. For medical intervention, CPR buys vital time. Every second without oxygen results. Good CPR greatly lowers brain injury risk.Training guarantees a correct CPR oxygen supply. Perfect depth and pace enhance oxygen flow. Quick response helps to sustain brain function better. CPR is lifesaving because of its oxygenating ability. Anyone can learn to keep the oxygen flow continuous.Simple acts help to preserve oxygen, hence preventing harm. Good CPR saves brains every day. This makes CPR training very necessary for everyone. Immediate CPR Doubles or Triples Survival Rates: In heart attacks, every minute counts. Quick CPR greatly increases chances of survival. Research shows early intervention saves lives. Fast actors among bystanders provide greater results. Effective compression preserves vital blood flow. Oxygen keeps reaching crucial organs. There is far less chance of brain injury.Without fast CPR, survival rates drop. The early minutes define the recovery possibility. Good chest compressions buy important time. They close the discrepancy till EMS shows up. AED usage, together with CPR, performs best.Trained responders help communities to see more survival. Simple acts produce outcomes that change lives. This essential ability is teachable to anybody. Good training helps one to develop confidence. Muscle memory starts to play in emergencies. Don’t delay; start compressions right away. Fast and hard in the middle. Your acts immediately affect the chances of survival. Be the differentiator between life and death. CPR instruction turns average individuals into lifesavers.The figures are not lying. Instant answer either doubles or triples the possibilities. Therefore, an understanding of CPR becomes rather important. Raise knowledge and help more people to survive. CPR Works Alongside AEDs for Maximum Effectiveness: For cardiac arrest, CPR maintains blood flow. AEDs shock based on cardiac rhythms. Collectively, they represent the gold standard for survival. Until the AED is available, CPR keeps the organs oxygenated. The gadget leads consumers precisely through every stage. Between shocks, chest compressions keep circulation flowing. Double AED efficacy with immediate CPR. Using both rapidly increases survival rates.AEDs require CPR support; they cannot function by themselves. Compressions prime the heart for defibrillation. Every step in CPR lowers the possibility of success. Good cooperation between both saves more lives. Trained responders move between approaches fluidly. Public AED availability mixed with bystander CPR generates potentially life-saving power.In a heart attack, seconds count. Up to defibrillation, CPR closes the gap. This potent mix stops brain damage. Communities need easily accessible tools as well. Training guarantees confident application in a crisis. CPR and AEDs taken together give the highest chance for revival. Anyone Can Perform CPR – No Medical Background Needed: Saving a life does not call for medical knowledge. Anyone can learn and use simple enough CPR to be effective. Hands-only CPR eliminates that complexity. Just quick and hard on the chest’s center. The American Heart Association attests that unskilled onlookers can save lives. Even flawed CPR greatly increases the odds of survival. Young children as young as nine have done CPR well. Smartphone apps today help consumers take the correct approach. The Good Samaritan Law guards those who volunteer honestly. Though action saves lives, hesitation kills. Ten percent less survival results from every minute without CPR. Until aid comes, your two hands can keep someone alive. Usually occurring at home, most cardiac arrests might rescue a loved one. Free internet lessons cover the foundations in minutes. Workplace and community training produce life-saving agents all around. You can be someone’s hero right now without a second thought. CPR Buys Time Until Professional Help Arrives: While the heart pauses, CPR maintains oxygen flow. Every compression forces blood
7 Essential Steps of CPR Everyone Should Know
Knowing the CPR steps for adults can mean the difference between life and death in emergencies. The basic CPR procedure involves a combination of chest compressions and Automated External Defibrillator (AED)rescue breaths to maintain blood flow. Learning how to perform CPR correctly ensures you act confidently when seconds matter. The American Heart Association (AHA) sets the latest CPR guidelines for 2024, emphasizing proper technique and timing. A key debate centres on hands-only CPR versus rescue breaths, with hands-only being simpler for untrained responders. Mastering the CPR chest compression technique, pushing hard and fast at a compression rate of 100-120 per minute, is critical. Incorporating the use of an Automated External Defibrillator (AED) with CPR steps significantly boosts survival rates. Proper CPR training and certification, such as Basic Life Support (BLS), prepare you for real-life scenarios. Understanding the difference between infant, child, and adult CPR ensures an age-appropriate response. Avoiding common CPR mistakes, such as shallow compressions or delays, improves outcomes. Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) is a vital link in the Chain of Survival, bridging the gap until Emergency Medical Services (EMS) arrive. The Good Samaritan Law protects bystanders who assist in good faith. Whether you’re a healthcare provider or a concerned citizen, mastering these steps empowers you to save lives. This guide clearly and concisely breaks down the seven essential steps. Stay prepared; your actions could be the difference between life and death until professional help arrives. 7 Essential Steps of CPR Everyone Should Know Assess the Scene for Safety: Ensure the surroundings are safe and protect yourself before initiating CPR. Look out for quick threats, such as traffic, fire, electrical hazards, or unstable buildings. Never rush into a dangerous scenario; you cannot assist if you fall prey as well. Should risks exist, either eliminate them or, if at all feasible, relocate the patient to a safe area. Then tap the victim’s shoulder and yell, “Are you okay?” to gauge their reaction. Look for normal breathing by watching their chest for 5-10 seconds. Call Emergency Medical Services (EMS) right away if they are nonresponsive and not breathing regularly. If others are there, assign someone else to call while you start CPR. Examining the situation also means looking for possible medical hints. Search for trauma indicators, medicine bottles, or medical wristbands. This knowledge enables responders to deliver more effective treatment. Ensure you have sufficient space to kneel and perform proper chest compressions. If necessary, take off the victim’s chest-restricting clothes. Scene safety, after all, also includes shielding yourself from body fluids. If at hand, use a CPR mask or barrier device. Although you prioritize universal precautions, the Good Samaritan Law protects rescuers who act in good faith. While reducing dangers, a rapid yet thorough safety inspection ensures effective intervention. Only start CPR after the location is under guaranteed security. Spending a few seconds to evaluate the situation might help prevent further damage and increase the victim’s chances of survival. Check for Responsiveness and Breathing: When someone is unresponsive, first rapidly evaluate their awareness and breathing before beginning CPR. To get a reaction, forcefully tap their shoulder and yell, “Are you okay?” If they do not respond, quickly look for signs of regular breathing. Look for chest movements; listen for breaths; feel for air coming from their nose or lips. Either frequent gasps or no breathing suggests that CPR has to start immediately. Time is of the essence; every second without oxygen reduces survival prospects. Contact emergency services (or advise someone close to contact) and begin CPR if the sufferer is unconscious and not breathing regularly. Agonal breathing, sometimes referred to as snoring or coughing, is not normal breathing; it should be addressed as a sign of cardiac arrest. Place someone in the recovery position on their side to maintain an open airway if they are unconscious but breathing regularly. Watch them till aid shows up. Start CPR right away if at any moment they stop breathing. Key actions: Shout and tap to check responsiveness. Look, listen, and feel for breathing for no more than 10 seconds. Call for help if the person is unresponsive and not breathing. Start CPR when you detect no normal breathing. This phase guarantees that you never slow down life-saving chest compressions. Correct evaluation guarantees a rapid response for patients in cardiac arrest and helps to avoid needless CPR on a breathing patient. Act quickly; your reaction could save a life. Call Emergency Services (911 or Local EMS): Your first concern becomes phoning emergency services after you confirm an unresponsive victim. Call 911 (or your local emergency medical services number) if you are alone. If others are present, ask someone to call while you begin CPR. This guarantees the fast arrival of skilled assistance. Inform the dispatcher of important information, including the victim’s condition, location, and any potential risks in the area. Until advised otherwise, please remain on the line, as they will guide you through AED usage or CPR procedures. In cardiac crises, time is of the essence; every minute without CPR lowers survival rates by 7 to 10%. If the victim is a youngster or a drowning victim, start two minutes of CPR, then contact EMS. This exemption applies to oxygen shortages in specific situations. Keep the phone on speaker if possible; dispatchers often provide life-saving advice. Never miss calling completely, and never postpone CPR for too long. Medications and defibrillators, among other tools used by Emergency Medical Services (EMS), greatly enhance results. Recall that early access to EMS is as much a component of the Chain of Survival as early CPR. Your brief contact closes the distance separating collapse from hospital treatment. Follow the dispatcher’s directions exactly; their training is to assist inexperienced rescuers. Send someone to get an AED while you keep compressions on target. Stay calm, speak clearly, and believe that your efforts keep the sufferer alive until experts arrive. Position the Victim Correctly for CPR: Effective cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) relies on maintaining the correct posture. Start by laying the sufferer down
What is BLS? Understanding Basic Life Support for Health Care Providers
Healthcare practitioners must possess the essential skill of Basic Life Support (BLS), which includes lifesaving methods such as cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and the use of automated external defibrillators (AEDs). Nurses, physicians, and Emergency Medical Technicians (EMTs) are more prepared to handle life-threatening situations when they have completed Basic Life Support training. The importance of BLS in healthcare relies on its ability to save lives in hospitals and healthcare facilities. Sign up for a class at 141 Protection Training, a top facility for CPR and AED training, to become a BLS-certified professional. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has established requirements for BLS certification for healthcare providers, and many nursing schools and medical colleges now demand it. Basic Life Support (BLS) lays more emphasis on the fundamentals than Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support (ACLS). Enroll at CPR and AED training centers like 141 Protection Training to master lifesaving skills and earn your BLS certification today. The American Heart Association (AHA) and the Red Cross BLS Certification are influential groups that establish norms. Feel confident saving lives by enrolling in a first responder training program with 141 Protection Training. Why is BLS Important in Healthcare? Because BLS can save lives in situations such as Sudden Cardiac Arrest (SCA), it is essential in the medical field. Prompt BLS intervention helps maintain oxygen and blood flow to vital organs, preventing death and brain damage. Emergency Medical Technicians (EMTs), physicians, nurses, and other healthcare professionals rely on BLS to respond effectively in hospitals and various healthcare environments. The American Heart Association (AHA) states that early BLS can double or triple survival rates. Additionally, BLS ensures compliance with OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) regulations. Mastering BLS equips healthcare workers to become competent first responders who can take immediate action in emergencies. 141 Protection Training now offers BLS training for nurses and doctors. BLS vs CPR Certification: What’s the Difference? This table lists the main distinctions to assist you in selecting the best certification for your requirements. Enroll in 141 Protection Training right away for BLS certification for healthcare providers! Point of Difference BLS Certification CPR Certification Target Audience Healthcare providers (nurses, doctors, EMTs, etc.). General public (parents, teachers, bystanders, etc.). Scope of Training Includes CPR, AED use, choking relief, and team dynamics for multi-rescuer scenarios. Focuses on basic chest compressions and rescue breaths. Complexity Advanced techniques tailored for healthcare settings. Basic techniques for everyday emergencies. Certification Validity Typically, valid for 2 years. Usually, valid for 2 years. Recognition Recognized by the American Heart Association (AHA) and Red Cross BLS Certification. Recognized by organizations like the AHA and Red Cross. Who Needs BLS Certification? BLS training for nurses and doctors is essential, but it’s also critical for other healthcare roles, including: Emergency Medical Technicians (EMTs) Paramedics Medical students Dentists First responder training programs participants BLS certification for healthcare providers who respond to medical crises is mandatory. Emergency Medical Technicians (EMTs), paramedics, physicians, nurses, and medical students are all included in this. BLS certification is a requirement for several medical institutions and nursing schools. BLS training is also beneficial for participants in first responder training programs, dentists, and physical therapists. To comply with Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) regulations, healthcare personnel in hospitals and other healthcare institutions must also keep their BLS certification current. BLS training for nurses and doctors guarantees that you are ready to save lives, regardless of your level of experience. Become a qualified lifesaver by enrolling in 141 Protection Training right now! Who Needs BLS Certification? The Basic Life Support (BLS) certification is an easy way to get the skills that can save lives. This is a detailed tutorial: Pick a Reliable Training Provider:Learn CPR and how to use an automated external defibrillator at 141 Protection Training or another approved facility. Choose a Program:You can choose between an in-person and an online BLS certification based on your schedule and personal preferences. Finish the Course:Learn how to perform CPR, rescue breathing, use an automated external defibrillator (AED), and deal with choking. The courses also include healthcare team dynamics. Pass Your Evaluation:Take both a written test and an oral exam to prove that you’ve learnt the material. Advance to the Certified Level:A basic life support (BLS) certification that is good for two years will be yours when you pass. 141 Protection Training guarantees your complete preparedness by designing courses that fulfil the requirements of the American Heart Association (AHA) and the Red Cross BLS Certification. Becoming a certified lifesaver is within your reach; enroll today! Why Choose 141 Protection Training for BLS Certification? Premier-notch BLS certification for healthcare providers is available at 141 Protection Training, a premier CPR and AED training facility. Our courses follow the latest standards of Red Cross BLS Certification and the American Heart Association (AHA) for current training. Prepare yourself to successfully manage crises with the help of our skilled teachers, plenty of hands-on practice, and realistic scenarios. Our BLS training for nurses, doctors, and EMTs meets Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) criteria. Convenient learning alternatives include online BLS certification. If you want to become a certified lifesaver at a cheap price, 141 Protection Training is the place for you! Frequently Asked Questions: What does BLS mean? BLS means Basic Life Support, a set of lifesaving skills for healthcare providers. Who requires BLS certification? Healthcare providers like nurses, doctors, and EMTs require BLS certification to respond to emergencies effectively. How does BLS differ from CPR? BLS includes advanced techniques like team dynamics and AED use, while CPR focuses on basic chest compressions and rescue breaths. Where do I get BLS certified? Enroll in a course at 141 Protection Training, a leading CPR and AED training center. What skills does BLS training teach? BLS training teaches chest compressions, rescue breaths, AED use, and choking relief for adults, children, and infants. How long does BLS certification remain valid? BLS certification remains valid for two years before requiring renewal. Can I complete BLS training online? Yes, 141 Protection Training offers online BLS certification for flexible learning options. Why
What is CPR? | Learn the Basics of Life-Saving CPR
In cases of life-threatening crises, such as Sudden Cardiac Arrest (SCA), the goal of cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is to bring oxygen and blood back to the brain and other critical organs. This cardiopulmonary resuscitation guide walks you through the CPR steps and techniques, including how to perform CPR, including CPR for adults and children. The importance of CPR involves both hands-on compressions and rescue breaths. It is very important to administer cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) promptly since it can increase survival chances by two or three times. Learn Hands-Only CPR at trusted CPR Training Centres like 141 Protection Training to assist until Emergency Medical Services (EMS) arrive and save lives effectively. CPR guidelines and updates are provided by organizations like the American Heart Association (AHA) and the Red Cross CPR Certification Programs to assure efficacy. Basic Life Support (BLS) for healthcare professionals, Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support (ACLS) for advanced treatment, and Pediatric CPR for infants and children are all included in the training. The use of an Automated External Defibrillator (AED) is also included in CPR training and certification courses provided by authoritative CPR training institutions. With the knowledge you get during CPR and first aid training, you can confidently respond to crises, regardless of Hands-Only CPR vs traditional CPR. Take a class now and earn your lifesaving certification! What is CPR? Sudden Cardiac Arrest (SCA) stops breathing or heartbeat, requiring CPR techniques to restore circulation. Perform rescue breathing and chest compressions to keep oxygen and blood flowing to vital organs. Every second counts when the heart stops, as brain damage begins within minutes and death follows quickly. If the patient cannot breathe, perform CPR to maintain circulation until EMS, medical personnel, or an AED arrive. The American Heart Association (AHA) states that quick CPR doubles or triples a victim’s survival chances. Anyone, trained or not, can perform CPR, making it a crucial life-saving skill. Knowing CPR empowers you to save lives during emergencies. Why is CPR Important? Performing cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) prevents death by keeping oxygen and blood flowing to the brain during cardiac arrest. Act immediately to double or triple your survival chances. Immediate and permanent brain injury or death can occur in the absence of cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR). Bystanders performing cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) may contact Emergency Medical Services (EMS) quickly. It enables regular people to take charge in times of crisis. Any setting, be it a house, a workplace, or a public venue, might have a cardiac arrest. Always be ready to aid, whether a loved one or a stranger, by knowing CPR. The American Heart Association (AHA) and similar groups stress their potential to save lives. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) supports the use of an AED or automated external defibrillator. Training enhances both confidence and competence under pressure. Enrolling in a course to become a certified CPR provider to acquire these vital abilities. Take immediate action and make a difference in people’s lives! Aspect Hands-Only CPR Traditional CPR Definition Continuous chest compressions without rescue breaths. Combines chest compressions with rescue breaths. When to Use Ideal for untrained bystanders or those uncomfortable with rescue breaths. Recommended for trained individuals or specific cases like drowning. Technique Push hard and fast (100-120 compressions per minute) on the center of the chest. 30 chest compressions followed by two rescue breaths. Effectiveness Maintains blood flow to the brain and vital organs. Provides oxygen to the lungs and blood flow to the brain. Best For Adults and teens experiencing Sudden Cardiac Arrest (SCA). Infants, children, and cases of respiratory arrest (e.g., drowning). Training Required Minimal training; easy to learn and perform. Requires formal training and certification. Recommended By American Heart Association (AHA) for untrained bystanders. AHA and Red Cross for trained responders. Equipment Needed None (unless an AED is available). None (unless an AED is available). Goal Buys time until EMS or an AED arrives. Provides oxygen and blood flow until professional help arrives. CPR Steps and Techniques: Assess the Situation: Check for responsiveness and breathing. Call for Help: Dial 911 or ask someone to call Emergency Medical Services (EMS). Begin Compressions: Place hands on the center of the chest and push hard and fast (100-120 compressions per minute). Provide Rescue Breaths: Tilt the head back, lift the chin, and give two breaths after every 30 compressions. Use an AED: Attach the device and follow its instructions. With Children (Pediatric CPR) in Mind: Compress with two fingers and breathe gently as directed by the American Heart Association and the Red Cross CPR Certification guidelines. CPR Training and Certification: Our courses accommodate all experience levels, including parents, teachers, and healthcare professionals. Learn effective CPR procedures based on guidelines from the American Heart Association (AHA) and the American Red Cross. We offer Basic Life Support (BLS), Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support (ACLS), Pediatric CPR, and Hands-Only CPR. Our courses teach the use of AEDS, chest compressions, and rescue breaths through expert instruction and hands-on practice. Gain confidence in responding quickly to Sudden Cardiac Arrest (SCA) or choking emergencies. Earn a nationally recognised, two-year CPR certification from 141 Protection Training. CPR certification benefits careers, classrooms, and personal preparedness. Start learning CPR today; you never know when you’ll need it. Enroll in 141 Protection Training now and become a certified lifesaver. Frequently Asked Questions: What does CPR mean? CPR means Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation, a technique that saves lives during emergencies like cardiac arrest. Why should I learn CPR? Learning CPR prepares you to save lives during emergencies like Sudden Cardiac Arrest (SCA) or choking. What steps do I follow to perform CPR? Perform chest compressions and rescue breaths to maintain blood flow and oxygen to the brain. How does Hands-Only CPR differ from traditional CPR? Hands-Only CPR uses only chest compressions, while traditional CPR combines compressions with rescue breaths. Can I use CPR on children and infants? Use pediatric-specific techniques like Pediatric CPR for infants and children. What does an AED do during CPR? An Automated External Defibrillator (AED) delivers a shock to restore a normal heart rhythm during cardiac arrest. Who updates CPR guidelines regularly? Organizations like the American Heart Association
How to Perform Hand-Only CPR? Quick Guide
To be prepared to respond to emergencies, learning the hands-only CPR steps is essential. CPR without mouth-to-mouth refers to a straightforward approach that teaches participants how to perform CPR correctly, focusing on chest compressions only. In addition to Emergency CPR techniques, this approach clarifies when to use hands-only CPR and serves as an effective tool for CPR in cardiac arrest victims. Reliable CPR procedures for adults are ensured by following compression-only CPR guidelines and bystander CPR instructions. The American Heart Association (AHA) endorses Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) as a life-saving measure, especially during Sudden cardiac arrest (SCA). Victims can be stabilized until Emergency Medical Services EMS arrives by using an automated external defibrillator (AED) in conjunction with adequate chest compressions. Hands-only CPR training equips rescuers to act promptly during Out-of-hospital cardiac arrest, reinforcing Bystander intervention and timely 911 emergency response. Earning these skills can help you feel more confident in life-or-death situations. By consistently performing Hands-only CPR training, you strengthen your preparedness to act rapidly and efficiently during emergencies. Steps of Hand-Only CPR: Master the steps of hands-only CPR to provide immediate aid during cardiac emergencies. Check responsiveness, call 911, and perform continuous chest compressions until help arrives, and follow the following steps: Get Assistance As soon as you see a person who is not breathing regularly and is unresponsive, dial 911 for emergency services. Start performing Hands-Only CPR and instruct someone nearby to dial 911. Inform the dispatcher exactly where the victim is located and their current condition. Have someone bring an AED (Automated External Defibrillator) to the location if one is available. Quickly access medical assistance and an automated external defibrillator (AED) to improve the victim’s prognosis drastically. In a crisis, every second matters, so respond quickly and assuredly. If you need sophisticated medical treatment quickly, the chances of a good outcome improve when you contact for aid immediately. Placing the Victim It is important to position the victim appropriately to perform hands-on CPR effectively. Lay the patient on their back on a firm, level surface. Avoid soft surfaces, such as couches and mattresses, to ensure your chest compressions are as effective as possible. Kneel and position your hands directly over the victim to gain the best leverage. Maintaining this position allows you to apply the ideal amount of pressure and depth during compressions. Proceed cautiously when lowering the individual from a high surface to the ground. By positioning yourself correctly, you can maximize the effectiveness of your chest compressions, increasing the likelihood of survival until emergency medical services (EMS) arrive. Respond swiftly and focus on the victim’s safety to significantly improve their chances of survival. Start Chest Compressions Hand Placement: Place the heel of one hand on the center of the chest (between the nipples). Place your other hand on top and interlock your fingers. Compression Depth: Push down at least 2 inches (5 cm) but no more than 2.4 inches (6 cm). Compression Rate: Perform compressions at a rate of 100-120 per minute. Proceed with Compressions Continue chest compressions without interruption until EMS arrives or the patient shows signs of life. At a rate of 100–120 compressions per minute, press down forcefully on the center of the chest, ensuring your fingers go at least 2 inches (5 cm) deep. To restore blood flow to the heart, allow the chest to fully recoil between compressions and avoid applying any pressure when recovering. If an AED becomes available, take a moment to use it; after delivering a shock, quickly resume compressions. If you begin to feel fatigued, ask another bystander to assist you in maintaining your compressions. Do not stop until medical personnel arrive; your efforts may increase the patient’s chances of survival by two to three times. Learn cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) with the experts at 141 Protection Training to gain the confidence to save lives easily! Why Use Hands-Only CPR? The American Heart Association (AHA) recommends Hands-Only CPR for untrained bystanders or those uncomfortable giving rescue breaths. This method’s streamlined procedure allows anybody to respond swiftly to life-threatening situations like Sudden Cardiac Arrest (SCA). Hands-only CPR improves prognosis by delivering chest compressions that maintain blood flow to the brain and vital organs. Reducing mortality rates by half or even a third is possible with rapid chest compressions, according to studies. Bystanders step in at critical times, using Hands-Only CPR, which eliminates hesitation to perform mouth-to-mouth rescue breaths. It’s accessible to everyone, anywhere, and anybody can learn how to do it. 141 Protection Training offers comprehensive CPR certification classes, including instruction on rescue breaths and AED use, for individuals seeking in-depth training. Sign up now to get the self-assurance and lifesaving abilities you require! Get Certified: 141 Protection Training offers complete CPR certification, but Hands-Only CPR remains a crucial lifesaving skill. Our training covers the use of AEDs, chest compressions, and rescue breaths to prepare you for emergencies. Earn your confidence and proficiency with the help of certified teachers who lead you through real-world scenarios and hands-on practice. Certification ensures that parents, teachers, and safety officers adhere to the standards set by the American Heart Association (AHA) and the American Red Cross. Don’t wait until you’re in a true crisis to become a certified lifesaver; sign up now. Contact 141 Protection Training immediately to reserve your position and start making a positive impact! Frequently Asked Questions: What does Hands-Only CPR involve? Hands-Only CPR involves performing continuous chest compressions without rescue breaths to maintain blood flow during cardiac arrest. When do I use Hands-Only CPR? Use Hands-Only CPR when an adult or teen suddenly collapses and shows no signs of responsiveness or normal breathing. How do I position my hands correctly for Hands-Only CPR? Place the heel of one hand on the center of the chest and stack the other hand on top, interlocking your fingers. How deep do I compress the chest during Hands-Only CPR? Compress the chest at least 2 inches (5 cm) but avoid exceeding 2.4 inches (6 cm). What rate do I maintain for chest